
 |
All About Firewalls |
|
|
Firewall(fīr´wâl) (n.) A system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. Firewalls can be implemented in both hardware and software, or a combination of both. Firewalls are frequently used to prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets. All messages entering or leaving the intranet pass through the firewall, which examines each message and blocks those that do not meet the specified security criteria. 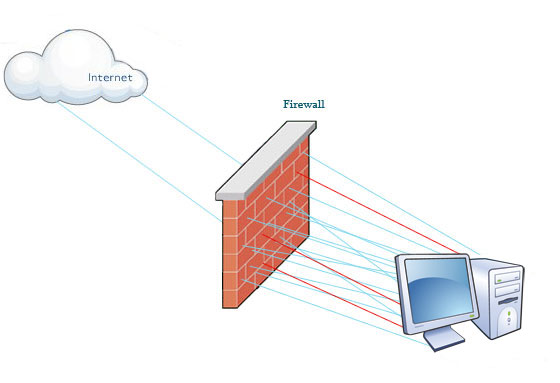 In non-computer industries, a firewall is a specially designed wall that controls the spreading of a fire. In networking, a firewall could be described as a specially designed device that controls the spreading of a network threat. The most commonly talked about source of network threats is the Internet. The Internet is the home of many unknown people that we cannot trust. There are hackers on the Internet that may want to do our networks harm. We can use a firewall to impede an untrusted person from doing damage to our networks. A more textbook definition of a computer firewall is that it is a method or device that regulates the level of trust between two or more networks. A firewall can consist of software, hardware or a combination of both. A firewall can protect your network from the Internet as well as regulate the traffic between networks within the same company. For instance, a firewall can allow the legal department's network to have access to the marketing file server but the marketing department can be refused access to legal. In this example the firewall is positioned between the marketing and legal networks so that all communication must pass through the firewall. The firewall is then able to ensure that only authorized packets are allowed. There are several types of firewall techniques: In practice, many firewalls use two or more of these techniques in concert. A firewall is considered a first line of defense in protecting private information. For greater security, data can be encrypted. |